Torque:
Torque: A measure of the force that can cause an object to rotate about an axis
The Counter-clockwise torque is positive while clockwise torque is negative
Only the perpendicular component of force will apply a torque
The units of torque are Joules
Torque Applications:
Balance:
Remember to account for clockwise/counter-clockwise rotation when doing torque problems
To balance weights on a bar/seesaw, equal the sum of the torque on the left and the right must equal to zero
The closer the weight is to the center, the less torque it applies
Lever:
The closer the item being lifted is to the fulcrum, the less force is needed to move it
Screwdriver/Circle:
The greater the radius of a circle, the less force needed to exert the same amount of torque
Moment of Inertia:
Moment of Inertia: An object’s resistance to angular acceleration due to an applied torque
Angular acceleration and moment of inertia are inversly related
There are various values of I (Inertia) depending on the object’s shape and axis of rotation
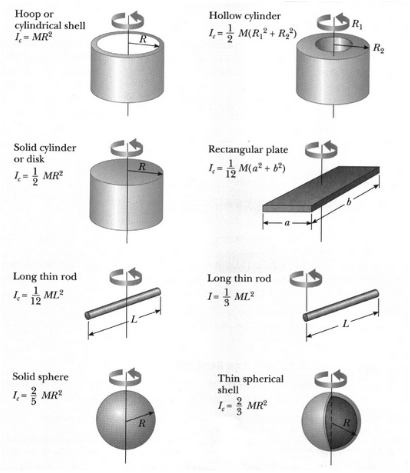
Parallel Axis Theorem:
If the moment of inertia about the center of mass is known